Table of Contents
What is Non-Woven Fabric?
In recent years, nonwoven fabrics have grown in importance as a component of the textile industry. Non-woven fabric, in its most basic form, is a type of fabric that lacks the intertwined strands that characterize standard woven fabrics. Although the fabric has an orderly internal structure, it is largely manufactured by weaving threads together and then combining them using one of the many possible processes to create a unified material that is identical to the traditional fabric we use. However, non woven fabrics do not require knitting or weaving; instead, it is treated mechanically, chemically, or thermally to bring the fibers together in a cohesive fabric.
Characteristics Of Non-Woven Fabric
A nonwoven fabric’s specific set of qualities is determined by a mix of elements during its manufacture.
- Non-woven fabrics can have a paper-like, felt-like, or comparable appearance to woven materials.
- They can have a soft, pliable hand or a firm, rigid, or broad hand with little pliability.
- They might be translucent or opaque as well.
- Their porosity can range from very low tensile strength to very high tear and burst strength.
- They can be made by gluing, heat bonding, or sewing them together.
- The drapability of these materials ranges from excellent to non-existent.
- Some textiles are great for laundering, while others aren’t. It can be dry-cleaned.
Uses Of Non-Woven Fabric
Nonwoven products are becoming more popular. Nonwovens are used in a variety of applications, including disposables, durable consumer goods, and industrial materials. Because of its low cost and adaptability for a wide range of purposes, this type of goods is becoming increasingly popular in all of these fields.
- Disposable nonwovens are designed to be used just once; however, some, such as dust cloths, can be washed and reused multiple times.
- Personal hygiene goods, such as diapers and sanitary napkins; medical products, such as surgical gowns and drapes; surgical and industrial masks, bandages, wipes, and towels; bibs, and even special event outfits are all examples of general applications.
- Nonwovens with a long life span offer a wide range of uses. Both household goods and home furnishings, such as draperies, furniture upholstery, mattress padding, towels, table cloths, blankets, and carpet backing, and clothing and apparel, such as caps, linings, interlinings, interfacings, and the reinforcement of other fabrics, are examples of consumer durables.
- Filters, insulation, packing materials, roadbed stabilization sheeting or road-building materials, geotextiles, and roofing goods are only a few of the many industrial applications.
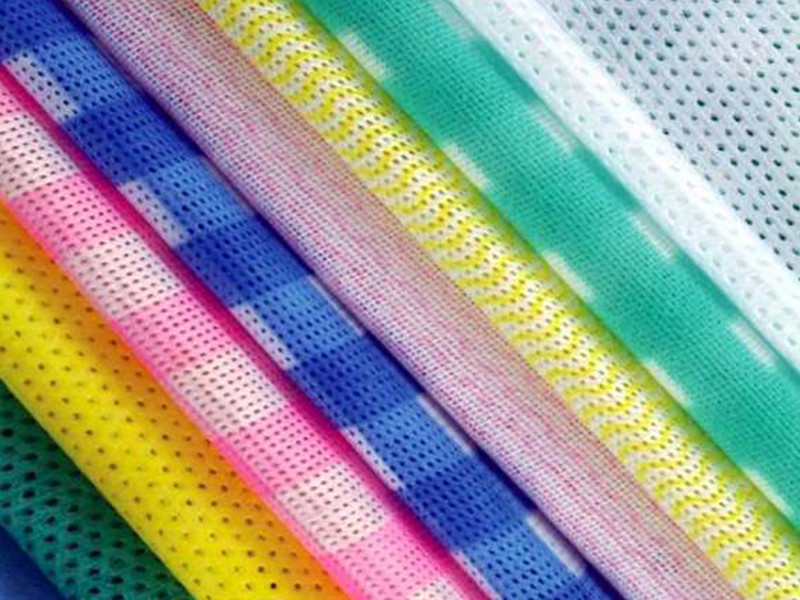

Advantages Of Non-woven Fabrics
Advantages:
- Lightweight: with polypropylene resin as the major raw material, the percentage is only 0.9, or three-fifths of cotton, with fleeciness and a nice feel.
- Non-toxic and non-irritating: the product is made with FDA-approved food-grade raw materials and has no other chemical additives. It has stable performance, is non-toxic, odorless, and does not irritate the skin.
- Antibacterial and anti-chemical agents: polypropylene is a chemically blunt substance that is not eaten by insects and can isolate bacteria and insect erosion in liquids; antibacterial, alkali corrosion, and completed products do not impact strength due to erosion.
- Excellent physical characteristics. Made of polypropylene spun straight into a net of thermal bonding products, the products’ strength is superior to that of regular staple fiber products, and the directionless strength is comparable to vertical and horizontal strength.
- Most nonwoven fabrics’ raw material is polypropylene, which is environmentally friendly. Furthermore, non-woven shopping bags can be reused more than ten times, and their environmental damage is only 10% that of plastic bags when they are discarded.
New Technology in Non-Woven Fabrics
Manufacturers frequently use nonwoven fabric production techniques such as felting and bonding for creating fabrics using new vegetable-based yarns, which have shorter staple fibers.
The felting procedure allows designers to create their unique fabrics. Non-woven fabrics are increasingly being employed in industrial applications, such as filtration systems, medical applications, and insulating purposes.
Non-woven fabrics created from newer fibers like Lyocell provide improved absorption and excellent wet strength for goods like medical swabs.